Contents
The sharing economy is a way for people to borrow or rent things from others instead of buying them. This is done through online platforms and can help save money and reduce waste.
The digital economy is ever-evolving, creating innovative business models that disrupt traditional industries. Two such models—sharing economy and online marketplaces—are often confused, despite their distinct characteristics.

The sharing economy
The sharing economy capitalizes on the peer-to-peer exchange of goods, services, and resources, focusing on access over ownership. This approach fosters sustainability and collaboration, offering more efficient use of resources. Platforms in the sharing economy often enable temporary sharing arrangements, such as renting a room on Airbnb, sharing a car through ZipCar, or hailing a ride on Uber. Many sharing economy companies have ties to the gig economy, creating flexible work opportunities for service providers.
These businesses have disrupted their respective industries, catering to millions of users worldwide.
Online marketplaces
Online marketplaces act as digital hubs for buying and selling goods and services between individuals or businesses. These platforms primarily focus on transferring ownership, encompassing a wide range of products and services, from physical items to digital offerings and professional services.
Some popular online marketplaces are Amazon, eBay, Etsy, and Alibaba. Although these platforms may create opportunities for entrepreneurs and small businesses, they aren’t intrinsically linked to the gig economy.
Key differences
- Sharing economy companies emphasize peer-to-peer sharing and prioritize access over ownership. In contrast, online marketplaces facilitate buying and selling, with ownership as the end goal.
- Sharing economy companies are more likely to be connected to the gig economy, offering flexible work opportunities for individuals providing goods or services. In contrast, online marketplaces might create entrepreneurial opportunities but aren’t directly tied to the gig economy.
- Sharing economy platforms frequently focus on underutilized or idle resources, efficiently using assets. Online marketplaces, on the other hand, can encompass a broader range of products and services, both new and used.
Why is the sharing economy important?
The sharing economy enables optimal utilization of assets, such as cars or homes, which may otherwise sit idle. By connecting owners with users, sharing platforms allow assets to generate income and reduce waste.
Sharing platforms often provide cost-effective alternatives to traditional services. For instance, ride-sharing services like Uber typically cost less than traditional taxis. At the same time, Airbnb offers more affordable accommodation options than hotels.
The sharing economy and the gig economy
The sharing economy has been a significant catalyst for the rise of the gig economy, creating new opportunities for flexible, non-traditional work. Both concepts are deeply interconnected, as the sharing economy’s rapid growth has led to an increasing demand for gig workers who can provide services on a per-task basis. This relationship has transformed how we think about work, enabling greater autonomy and flexibility for workers while raising concerns about worker rights and protections.
One of the key benefits of the gig economy is the opportunity it presents for individuals seeking alternative employment options. Gig workers can choose when, where, and how they work, enabling them to better manage their work-life balance. This flexibility can be particularly appealing for those who struggle to find full-time employment or must balance work with personal commitments, such as caregiving or education.
Moreover, the gig economy offers businesses new ways to scale their operations and manage labor costs. By hiring gig workers on an as-needed basis, companies can quickly adjust their workforce to meet changing demands without the long-term commitment of traditional employment contracts. This flexibility can increase efficiency and cost savings, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
Any concerns?
However, the gig economy also raises concerns about worker rights and protections. Gig workers are often classified as independent contractors rather than employees, which can exclude them from benefits such as minimum wage, overtime pay, healthcare, and paid leave.
Addressing the challenges of the gig economy requires a balanced approach that preserves its benefits while ensuring worker rights. This may involve redefining the legal classification of gig workers or implementing new regulations that mandate minimum standards for pay, benefits, and working conditions. Some jurisdictions have already started to enact such measures, like California’s Assembly Bill 5 (AB5), which established a stricter test for determining independent contractor status.
Successful sharing economy companies
The sharing economy has revolutionized how we work, live, and interact. As a result, numerous companies have emerged, disrupting traditional industries and transforming how we access services.
Airbnb: Reinventing the hospitality industry
Airbnb, founded in 2008, has become a household name in the short-term rental market. Through their innovative platform, users can rent their homes or rooms to travelers seeking unique and affordable accommodations. Airbnb’s success is driven by its ability to provide various lodging options tailored to different budgets and preferences. Additionally, the platform fosters a sense of trust and community among hosts and guests, further fueling its growth.
Uber: Transforming transportation
Uber, launched in 2009, has disrupted the transportation industry by connecting passengers with drivers through a user-friendly app. This peer-to-peer ride-sharing service has significantly impacted traditional taxi services, offering a more convenient, cost-effective, and personalized experience. Uber’s success can be attributed to its dynamic pricing model, efficient matching of drivers and riders, and constant expansion into new markets and services like food delivery and freight.
TaskRabbit: Streamlining the labor market
TaskRabbit, founded in 2008, is an online marketplace (sorry for the confusion) that connects users with local freelancers to perform various tasks, from assembling furniture to running errands. This platform has redefined how people access and provide services, offering flexibility, convenience, and a wide range of options for clients and freelancers. TaskRabbit’s success stems from its easy-to-use interface, comprehensive vetting process, and transparent pricing, which instills trust and reliability in the platform.
Additional Examples
- WeWork – redefining office space and coworking environments
- Turo – enabling car owners to rent out their vehicles to others
- Poshmark – facilitating peer-to-peer sales of fashion items and accessories
- Zipcar – providing car-sharing services for urban dwellers and businesses
- ThredUP – leading the way in the online secondhand clothing market
The success of these sharing economy companies demonstrates how innovative business models can disrupt traditional industries and reshape our lives. These companies have created platforms that foster trust, efficiency, and convenience for providers and consumers by leveraging technology.
As the sharing economy expands, we expect more companies to follow in the footsteps of Airbnb, Uber, and TaskRabbit.
The impact of COVID-19
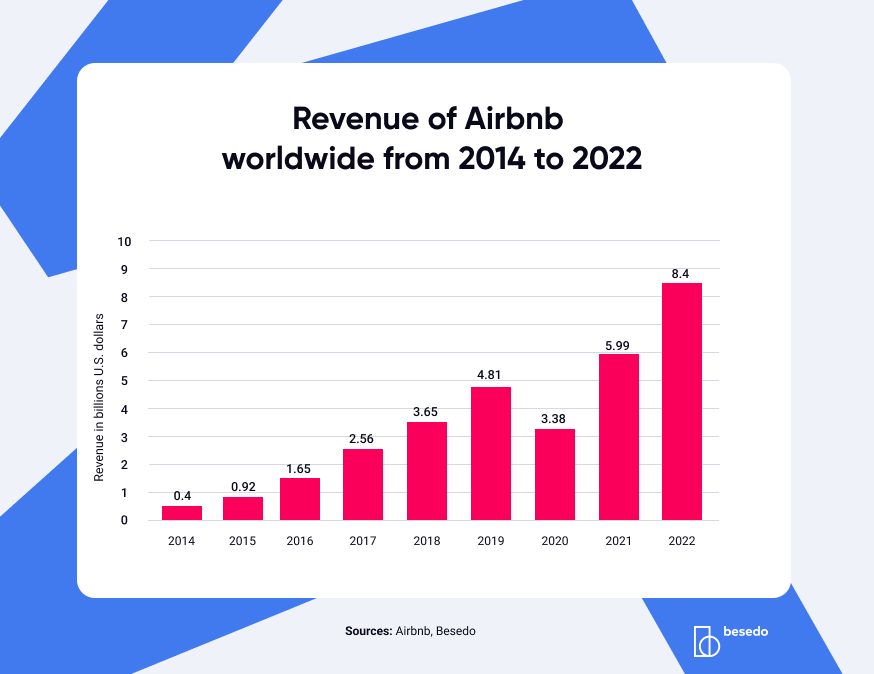
Let’s look at the enormous success of Airbnb for a minute. It’s impossible not to mention the impact COVID-19 had on the sharing economy – as opposed to online marketplaces.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially posed significant challenges to Airbnb, with the travel industry coming to a near standstill in early 2020. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, Airbnb introduced several measures to ensure the safety of guests and hosts and adapt to its user’s changing needs.
- Enhanced Cleaning Initiative: Airbnb launched an enhanced cleaning protocol for hosts, providing them with step-by-step guidelines on cleaning and sanitizing their spaces effectively. This initiative aimed to reassure guests of their safety while staying in Airbnb accommodations.
- Online Experiences: Recognizing the shift in demand for virtual experiences due to travel restrictions, Airbnb expanded its offerings to include online experiences. This allowed hosts to share their skills and passions with guests virtually, providing an alternative income stream and a unique way for people to connect during the pandemic.
As the world started to recover in 2021 and 2022 and adapt to the new normal, people began to prioritize flexible travel options, which played to Airbnb’s strengths. The company saw an increase in demand for longer stays, remote work accommodations, and unique stays, allowing it to bounce back and thrive post-pandemic.
Content moderation helps
Of course we will tell you that.
Of course.
Sharing economy platforms rely heavily on trust and user-generated content to build and maintain their reputation. Content moderation ensures that these platforms provide accurate information, credible reviews, and a safe user environment.
- Accurate information and reviews: User-generated reviews and ratings are essential for building trust in the sharing economy. Content moderation helps filter out fake reviews, spam, or other misleading content, ensuring that users can make informed decisions based on accurate and reliable information.
- Trust and safety: Sharing economy platforms often involve transactions between strangers. Content moderation is crucial in maintaining user safety by identifying and removing inappropriate, offensive, or harmful content and monitoring for potential scams or illegal activities.
- Protecting platform reputation and brand image: A well-moderated platform fosters trust and credibility among users, which is essential for the long-term success of sharing economy companies. Consistent content moderation helps protect the platform’s reputation and brand image by ensuring that user-generated content aligns with the company’s values and guidelines.
And content moderation is already helping some of the most successful companies. It doesn’t really matter the size of your company; we can all learn from those who are doing it right.
- Airbnb: The platform’s robust content moderation system checks for accurate property listings, reviews, and user-generated content. They also have guidelines on what types of content are acceptable and a reporting system for users to flag any inappropriate content or behavior.
- Uber: The ride-sharing platform uses content moderation to ensure the safety of both riders and drivers. They monitor user reviews and feedback to identify potential safety concerns, inappropriate behavior, or other issues. Uber also has a reporting system that allows users to report incidents or violations, helping maintain a safe and secure environment for all users.
- TaskRabbit: This platform connects users with local service providers for various tasks. TaskRabbit employs content moderation to verify the accuracy of user profiles, reviews, and task descriptions. They also have guidelines on what types of tasks are allowed on the platform and a reporting mechanism for users to flag any content that violates their terms of service.
Summary and key takeaways
We have probably all borrowed a toy or a game from a friend, right? That’s kind of like what the sharing economy is all about, but on a bigger scale. Instead of just borrowing things from friends, people use special websites or apps to borrow or rent things they need from other people they don’t know, like a bike or a room to stay in when they travel. This helps people save money, and it’s good for the environment too, because it means we don’t have to make new things all the time.
Content moderation is crucial for sharing economy companies to maintain trust, safety, and a positive user experience. Platforms can effectively mitigate risks by monitoring user-generated content and implementing clear guidelines and reporting mechanisms. By doing so, they protect their reputation and foster a thriving community of users.
Ahem… tap, tap… is this thing on? 🎙️
We’re Besedo and we provide content moderation tools and services to companies all over the world. Often behind the scenes.
Want to learn more? Check out our homepage and use cases.
And above all, don’t hesitate to contact us if you have questions or want a demo.




